Weather vs Climate
Climate change has been a part of Earth's history since the beginning. This has been confirmed by geologists and other scientists, who affirm that the Earth's temperature has been fluctuating naturally over tens of thousands of years. However, the recent changes that have been happening to the Earth due to industrialization have switched this process into accelerated mode.
This accelerated process of climate change has made it difficult for animal species to adapt and survive, including many communities around the world.
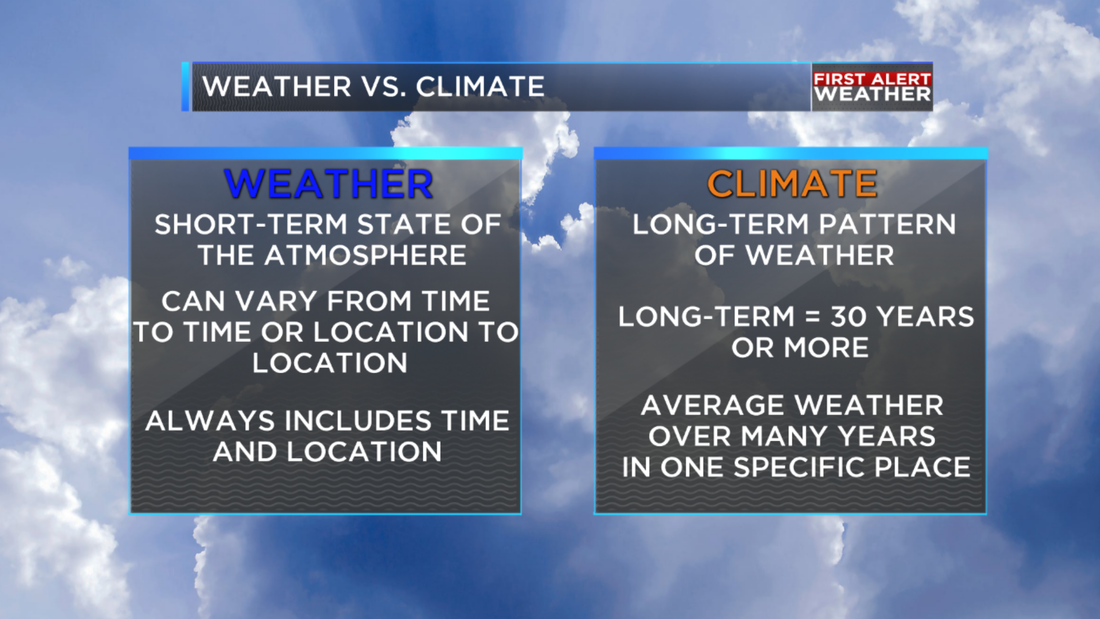
Let's start by reviewing the differences between weather and climate. Get your worksheet and let's complete it together!
This accelerated process of climate change has made it difficult for animal species to adapt and survive, including many communities around the world.
Let's start by reviewing the differences between weather and climate. Get your worksheet and let's complete it together!
Weather is defined by the atmospheric conditions including:
- Temperature
- Precipitation (rain)
- Wind, and
- Humidity
Climate is the average of the weather conditions in a region over a long period of time, like 30 years or more.
For instance, a region could have very hot summers with heavy snow during winter months, or four well-defined seasons, or a rainy season lasting three months; these are expected weather patterns.
A good way of thinking of these two factors is...
Climate is what you expect, while weather is what you get.
Many different factors determine the climate of a region.
On your worksheet, add the definitions of each factor:
Latitude: Lower latitudes (near the Equator) receive more direct sunlight, so these areas are hotter than higher latitudes.
Altitude: The air is thinner (has less Oxygen) and cooler in higher altitudes, such as mountains.
Land Formations: As clouds are blown over a mountain, they lose their moisture. One side of the mountain range will get rain, while the other will be dry.
Large bodies of water: Water heats and cools more slowly than land. Areas around lots of water have a smaller range of temperatures.
Air and Ocean currents: Warm currents heat the land they are near; cold currents cool that land.
The video below shows a quick report on what is normal and what isn't:
On your worksheet, add the definitions of each factor:
Latitude: Lower latitudes (near the Equator) receive more direct sunlight, so these areas are hotter than higher latitudes.
Altitude: The air is thinner (has less Oxygen) and cooler in higher altitudes, such as mountains.
Land Formations: As clouds are blown over a mountain, they lose their moisture. One side of the mountain range will get rain, while the other will be dry.
Large bodies of water: Water heats and cools more slowly than land. Areas around lots of water have a smaller range of temperatures.
Air and Ocean currents: Warm currents heat the land they are near; cold currents cool that land.
The video below shows a quick report on what is normal and what isn't:
Another issue we have been facing is the build-up of greenhouse gases. But what are greenhouse gases?
Let's go to the greenhouse gases page to learn more.
Let's go to the greenhouse gases page to learn more.
| weather_versus_climate.pdf | |
| File Size: | 18235 kb |
| File Type: | |